|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
TABLE OF CONTENTS
See you at Disney for the Cement Conference next Week
U.S. Cement Plants Choosing Lime Injection for HCl Control
Mercury Measurement and Control Part 1 – Hot Topic Hour March 28, 2013
Cemex to Pay $1.4 Million for Clean Air Act Violations - Wednesday, April 27, 2011
Yokogawa Information Management System Successfully Operates at Tsuruga Cement for Past Seven Years
Redecam Dry Lime SO2 Removal Used in Power and Cement Plants in Chile
GEA Bischoff Low Dust SCR System at Südbayer has been Operating for 2 Years
The 2013 IEEE-IAS/PCA Cement Industry Technical Conference will be held at the Walt Disney World Dolphin Resort, April 14–18, 2013. The exhibition is slated for the 15th and 16th. McIlvaine will be conducting interviews and taking pictures. Bob McIlvaine can be reached during the conference at mobile #847 226 2391.
A number of cement plants are opting for the use of hydrated lime to capture HCl as required by the new MACT rules. Here are some of the plants which have chosen this route.
|
STATE |
FACILITY NAME |
STREET |
CITY |
COUNTY |
CONTROL TYPE |
PERFORMANCE |
CONTROL START DATE |
NUMBER OF KILNS |
ANNUAL CAPACITY |
PROCESS TYPE |
|
CA |
9350 OAK CREEK RD |
MOJAVE |
KERN |
Dry lime scrub. Equivalent |
|
|
1 |
1,550,000 tpy |
Dry |
|
|
CA |
LEHIGH CEMENT CO. LLC, LEHIGH HANSON, INC., WEST REGION, PERMANENTE PLANT |
24001 STEVENS CREEK BLVD. |
CUPERTINO |
SANTA CLARA |
Dry lime scrub. Equivalent |
|
2012 |
1 |
1,521,000 tpy |
Dry |
|
CO |
3500 STATE HWY 120 |
FLORENCE |
FREMONT |
Wet Scrubber |
|
2007 |
1 |
1,900,000 Mtpy |
Dry, Preheater-Precalciner |
|
|
IA |
301 E FRONT ST |
BUFFALO |
SCOTT |
Dry lime scrub. Equivalent |
No inline raw mill, 4850.0 tons/yr |
|
|
|
|
|
|
IA |
LEHIGH CEMENT CO. LLC, LEHIGH HANSON, INC., NORTH REGION, MASON CITY PLANT |
700 25th Street |
Mason City |
Cerro Gordo |
Wet Scrubber |
1.01 lbs/ton clinker 30-day average |
1 |
938,000 Mtpy |
Dry |
|
|
IN |
Hwy 31 |
Speed |
Clark |
Dry lime scrubber Equivalent |
2013 |
2 |
1,050,000 tpy |
Dry |
Detailed plant and project information for cement is provided separately or as part of Industrial Emitters.
For more information click on:
201I Cement Plant and Project Tracking System
Sharon Sjostrom, P.E., Vice President Technology, ADA-ES LLC presented an overview of important considerations for achieving MATS compliance for mercury. Achieving consistent MATS compliance for mercury requires an integrated approach to plant operations. Fuel choices, boiler operations and technology choices for criteria pollutants and HAPS will affect mercury control and the ability to meet future regulations associated with ash and water.
Dr. James Staudt, PhD, President Andover Technology Partners, discussed the issues facing utility boilers, industrial boilers and Portland cement kilns that need to measure and control Hg emissions. Topics included:
|
Electronic CEMS |
Sorbent Traps |
|
§ Real-time measurement of Hg |
§ Lower capital cost |
|
§ Risk of lost data may be less |
§ Simpler, but need people trained in handling samples and selecting correct trap size and sample rate. |
|
§ EPA/ NIST protocol |
§ In principle, accurate to lower concentrations |
|
§ No need to send personnel up to collect/replace traps every few days. |
§ More consistent with RATA method of choice. |
|
§ Potential for process control |
|
Activated Carbon usage can be reduced through use of a feedback control system with an electronic Hg CEMS.
Bobby I.T. Chen, Client Program Manager, Integrated Emissions Solutions, at CB&I Shaw Environmental discussed “EMO™+HL, Total MATS Compliance Solution”. There are critical reasons to enhance mercury oxidization using CB&I’s technology because controlling mercury (Hg) emission from the coal combustion process is best achieved through a two-stage process. The first stage is to promote mercury oxidization at the combustion chamber outlet. The second stage is to provide absorbent to capture the oxidized mercury. On numerous of CB&I’s field EMO trials, EMO has been proven to achieve 90 plus percent Hg oxidization, thus facilitating the downstream AQCS Hg control efficiency. Furthermore, EMO was also found to be the most cost-effective way of controlling stack Hg.
Volker Schmid, PhD of Clean Air Engineering covered “Mercury Compliance Monitoring in 2015 and Beyond.” Monitoring mercury at the concentration levels specified by the new EGU MATS rules will be challenging for the cement and electrical utility industries, respectively. He made a case for using sorbent traps as the preferred alternative for mercury compliance monitoring for many of the facilities impacted by these requirements. Volker pointed to the accuracy of NIST calibrators which are an order of magnitude less accurate than what is needed in MATS. This is coupled with Hg CEMS inaccuracies which are also significant.
Capturing material over several days in a sorbent trap provides an accurate longer term measurement. It can be used with continuous mercury monitoring systems (CMMS) as a backup. The capital cost of sorbent traps is $100,000 to $150,000. This is less than half the capital cost of CMMS. Operating cost is $20,000-$30,000/yr and also about half that of CMMS.
The entire March 28, 2013 recording can be heard at:
Mercury Measurement and Control - Part 1 115
minutes
You will need to enter your name and email address after clicking link to
view recording.
Bios, Abstracts and Photos can be seen at: BIOS, ABSTRACTS, PHOTOS - 3-28-13.htm
The individual presentations are as follows:
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the U.S. Justice Department announced recently that Houston-based Cemex, Inc., one of the largest producers of Portland cement in the United States, has agreed to pay a $1.4 million penalty for Clean Air Act violations at its cement plant in Fairborn, Ohio, acquired by Cemex in 2000. In addition to the penalty, Cemex will spend an estimated $2 million on controls that will reduce nitrogen oxides (NOx) and sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions.
The settlement addresses modifications Cemex made to its plant without obtaining the proper permit, as required by the Clean Air Act. Major sources of emissions are required to obtain permits that require the installation of pollution control technology before making changes that would significantly increase air emissions. The settlement ensures that the proper control equipment will be installed to reduce future emission levels.
Cemex will install state-of-the-art control technologies at the Fairborn plant that will reduce annual emissions of NOx by approximately 2,300 tons and SO2 by about 288 tons. Reducing emissions from the largest sources, which include cement facilities according to EPA, is one of the agency's National Enforcement Initiatives for 2011-2013. The initiative continues EPA’s focus on improving compliance with the new source review provisions of the Clean Air Act among industries that have "the potential to cause significant amounts of air pollution." In fiscal year 2010, EPA claims, its enforcement actions in the cement manufacturing, coal-fired power plant, glass and acid sectors led to approximately 370 million pounds of pollution reduced or treated, $1.4 billion in estimated pollution controls, and $14 million in civil penalties.
Selective non-catalytic reduction equipment, along with operational modifications, will minimize NOx emissions, and lime spray absorber equipment will be installed to reduce SO2. This equipment will further reduce these two emissions, which are already below state and federal standards.
The proposed consent decree lodged with the United States District Court for the Southern District of Ohio, Western Division, is subject to a 30-day public comment period. More information on the settlement can be found at: http://www.epa.gov/compliance/resources/cases/civil/caa/cemexfairborn.html
Techno Tsuruga Co. Ltd. is an engineering and construction company in the Tsuruga Cement Group. Techno Tsuruga is engaged in electrical, machinery, construction, and civil engineering projects. Tsuruga Cement Co. Ltd., Techno Tsuruga’s parent company, produces high-quality cement using the most advanced manufacturing facilities and technologies. The product is shipped under the Taiheiyo Cement trade name to the nearby Hokuriku region as well as the Kinki region. Tsuruga Cement produces 140,000 tons of cement, 13,000 tons of calcium carbonate, and 11,000 tons of silica powder per month.
Techno Tsuruga was contracted by Tsuruga Cement to replace the legacy plant information management system at the company’s cement plant with a new one. The project scope included installation, application development, and maintenance.
In addition to obsolete hardware and software, the existing system had the following problems:
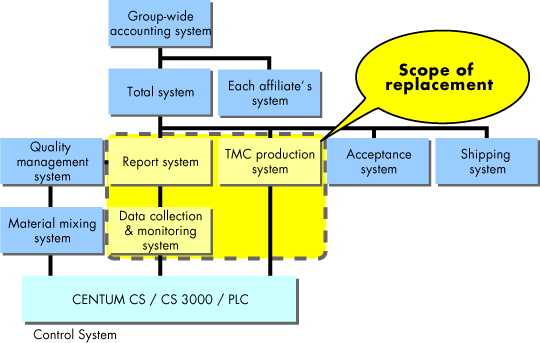
Plant-wide System Configuration
Techno Tsuruga adopted the Yokogawa Exaquantum system for the following reasons:
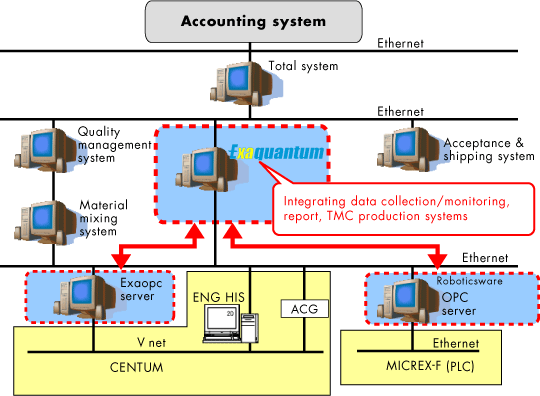
Exaquantum System Configuration
RESULTS: An overview screen and other operation monitoring screens were developed to provide an overview of plant-wide operation status and performance. Detailed screens are available from the main menu for confirming the operation of manufacturing equipment and the inventory status at a glance. Report and other function screens were also incorporated. The system has been proving itself since August 2005.
The E-CL generation company, controlled 52.7 percent by International Power plc group GDF Suez Latin-America, has replaced a precipitator with a Redecam fabric filter in coal-fired power Unit 1 (CTM1) operating in the Bay of Mejillones, north of the port of Antofagasta.
The bag filter installed in CMT1 is the first stage of a plan for a total investment of US$170 million to replace the previous electrostatic precipitators at coal-fired power plants in 12, 13, 14 and 15 located in Tocopilla.
With the E-CL project plans to reduce emissions in these units and meet the new standard that will be required for thermoelectric from 2013, which sets a maximum of 50 mg/m3 for particulate matter (PM2.5), 500 mg/m3 for nitrogen oxide (NOx) and 400 mg/m3 in the case of sulfur dioxide (SO2).
With the development of this initiative, E-CL, the largest electricity generator in the Far North, is moving forward to meeting the new emissions standards for power plants and expects to have installed the second bag filter in CMT2 in a year.
According to the findings by Vanni Boggio, Manager of Generation and E-CL sites, the process to install a new baghouse takes about a year, “and that engineering can take six to eight months, a period considered construction of the sleeves and new computers and then the installation phase and disarmament of former field electrostatic precipitator extends for another three months. "
For the development of project construction and installation of an SO2 removal system and bag filters, E-CL hired the Italian company Redecam. Asked about the choice of technology, the director of the Energy Business Unit Redecam Group, Giuliamaria Meriggi explains that the choice was between dry lime and semi-dry (spray driers). The Redecam dry technology was then selected. The executive said that this is a proven technology for Redecam for 30 years and has been applied also in Chile in Group Cement Polpaico and six continents (including Antarctica).
In March 2011, a new DeNOx plant was put successfully into operation at the German cement manufacturer Südbayer, Portland-Zementwerk (SPZ) in Rohrdorf.
The new selective catalytic reduction (SCR) system requires the operation temperature to be more than 250°C. To achieve this, the kiln exhaust gas is heated in heat exchangers supplied by Ecoflex, another member of the GEA Group.
The low dust DeNOx plant is the first of its kind in operation at a cement plant worldwide. Advantages of this arrangement after the dusting stage are lower operational cost and a longer lifetime of the catalyst.
Bob McIlvaine
President
847 784 0012 ext 112
rmcilvaine@mcilvainecompany.com
|
Copyright © 2011 McIlvaine
Company. All Rights Reserved Ph: 847-784-0012 | Fax; 847-784-0061
|