
Pharma Prospects
(Plants and projects with flow and treat
insights)
January
4, 2022
PRODUCTS
·
Containment Isolators & Glove Boxes
·
CraneCPE has intelligent solutions for diaphragm
valves
·
Validating safety of materials in single
use filters
·
Minimizing pump pulsation negative impacts
PROJECTS
·
Novo Nordisk plans $2.6bn pharma build with
engineering partner NNE
·
Britons expect continued collaboration in
(bio)pharmaceutical research
·
EMA launches the Regulatory Science Research
Needs initiative
·
ABPI publishes new roadmap to aid in ATMP
development
·
Plasma-based engineering to accelerate
antimicrobial material development
·
Reliable drug production requires fast and
GMP-compliant labelling
·
TRexBio Announces Collaboration with Janssen to
Discover Novel Targets for Immunology and
Inflammation
MARKETS
·
Guardtech Cleanrooms announces corporate
restructuring after acquisition
·
UK regulator publishes guidance on use of
real-world data to support clinical trials
·
Longest Running FDA-approved,
University-associated CDMO in the US
·
Aragen Life Sciences to Acquire Intox Pvt. Ltd.
·
Genmab Gains Broad Access to Synaffix's ADC
Technologies
·
Piramal Pharma Solutions Expands In Vitro
Capabilities at Ahmedabad Site
PRODUCTS
Containment Isolators & Glove Boxes
Manufacturing and handling highly potent
compounds requires specialized containment
capabilities with respect to personnel,
equipment and facilities. This, to protect the
drug product, the operators and the environment.
Most manufacturing processes for oral solid
dosage (OSD) drugs require some level of
containment. Nicomac is able to supply made in
Europe equipment for solid forms with high
containment capabilities or under isolators from
OEB3 to OEB5. The Nicomac designed, complete
line under isolators has been supplied with
great success all over the world. Automatic and
ergonomic sliding doors for an easy access to
the isolators requiring less space. All round
and smooth corners. High ergonomic handling
inside the isolator: FBD container moving on
rails from HSM to Mill, vacuum transfer from
container to Mill and from Mill to Blender.
Unique control system CFR21 part 11 compliant
for all granulation line and isolators.

·
Isolators for high containment designed for oel
up to 0.1 μg/m3
·
Isolators for Dispensing- Sampling- QC
·
Containment glove box
·
Certified exposure device operator
·
Pass box
·
Material transfer technology
·
Split butterfly valves
·
RTP rapid transfer port technology
Nicomac and partner specialized in isolator
technology joined their experiences, know-how
and their talent to design, develop, manufacture
and supply Isolation Technology to
pharmaceutical companies all over the world.
Nicomac is the right solution if you are looking
for isolators for solid forms
Nicomac has a specialized department with high
expertise & exceptional skill on Isolation
Technology for high containment
Nicomac success is due to the proven ability to
produce advanced tailor-made solutions that meet
client individual containment needs. Based on
European technology, Nicomac started designing
and manufacturing Isolators in 2004.
Nicomac has supplied and installed a completely
contained granulation line with 5 kg capacity,
for high potency products under isolator – OEL
level of 0.1 µg/m3 in 8 hours. An ergonomic and
high tech solution for:
·
Dispensing
·
HSM NicoMix
·
FBD NicoBed
·
NicoMill
·
Tumbler NiCO Mixers
·
Tablet press
·
NCS Coater
·
RTP Technology
CraneCPE has intelligent solutions for diaphragm
valves
SaundersVUE
offers intelligent solutions for
diaphragm valves specifically in the Life
Science industry. The platform is designed to
maximize plant efficiency by eliminating false
alarms and reducing set-up times. SaundersVUE
valve sensors provide a positive and accurate
The SaundersVUE suite of intelligent products
includes two valve sensors: • Saunders I-VUE:
Valve solution for end users due to enhanced
diagnostics and easy calibration • Saunders
M-VUE: For equipment manufacturers due to its
modular and compact design One feature that is
present in both SaundersVUE products is the
selfcalibration feature that holds potential for
cost savings. Traditionally, switchboxes require
two people for calibration, each taking around
30 minutes.
The maintenance personnel have to locate the
valve sensor in the field, open the enclosure
and then adjust the settings. This consumes a
lot of time, increasing maintenance costs.
However, with the new sensors, only one person
is needed to calibrate a sensor. This process is
very fast and efficient, taking only 3minutes,
as the need to open the enclosure is eliminated
because of the sensors’ contactless operation.
Validating safety of materials in single use
filters
Dr Sade Mokuolu, group compliance manager,
Watson-Marlow Fluid Technology Group has
addressed the importance of risk assessment in
qualifying SU components “As
detailed in USP 661.1, passing the
biocompatibility tests is not sufficient for a
complete risk assessment to be performed.
Understanding not just the material but the
propensity for the material to leach unwanted
and unknown chemicals into a drug product has
been a requirement of the industry in recent
times. This has been principally achieved
through extractables testing.
As the analytical technologies have advanced,
the techniques used to assess extractables and
potential leachables has become highly
developed. The analytical instruments are
extremely sensitive and are able to detect the
presence of compounds at levels in parts per
billion (ppb). These technologies are a far cry
from the wet chemistry tests reported in the
previous compendia.By providing the level of
technical/validation data about the component
material to the drug manufacturer early on
facilitates the adoption of SU technologies into
drug processes faster.”Her complete paper is
found at
https://pharmaceuticalmanufacturer.media/pharmaceutical-industry-insights/risky-business-the-importance-of-risk-assessment-in-the-sing/
Minimizing pump pulsation negative impacts
Gary Gaudet of DPS observes that “ there
are two types of pulsation; flow and pressure,
both have an effect on the customers
production, accuracy and reproducibility.
These effects can be minimized or amplified by
piping design and pressure control (i.e.
Equilibar). This is required to properly make
product (i.e vacines) or the increase yield in a
chromatography step”
Gay adds “Using different types of motors make a
difference in the performance of a pump. The two
types of motors are a digital/servo
motor or a asynchronous motor. The digital motor
does not only improve the accuracy of the pump
but also it’s range. An example of this is, the
pump had an original turndown of 30 to 1,
now, it has greater than 300 to 1 turn down The
accuracy was increased from 1 ½% to 0.5%.
This allows for better performance over a larger
range for Inline Dilution and Chromatography
skids“
The example below shows two types of pulsation;
flow and pressure, both have an effect on the
customers production, accuracy and
reproduceability. This is a low flow
pulsation pump that has a high pressure
pulsation.
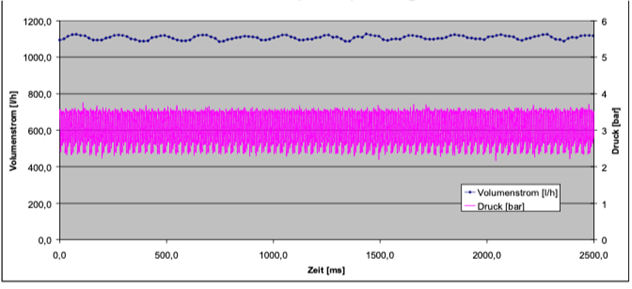
Gay adds “Using different types of motors make a
difference in the performance of a pump. The two
types of motors are a digital/servo
motor or a asynchronous motor. The digital motor
does not only improve the accuracy of the pump
but also it’s range. An example of this is, the
pump had an original turndown of 30 to 1,
now, it has greater than 300 to 1 turn down The
accuracy was increased from 1 ½% to 0.5%.
This allows for better performance over a larger
range for Inline Dilution and Chromatography
skids“
The next slide shows the difference between two
types of motors on the same pump,
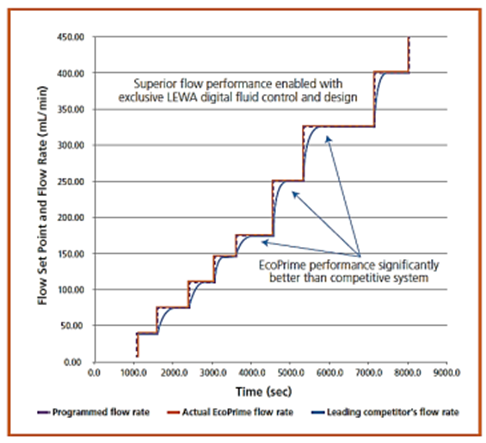
So, the pump types used depend on information or
biases at the customers site.
PROJECTS
Novo Nordisk plans $2.6bn pharma build with
engineering partner NNE
NNE is Novo Nordisk's engineering partner from
design to construction of this huge expansion
and has already delivered the conceptual and
basic design for the expansion of the Kalundborg
site
Novo Nordisk has announced its plans to invest
more than DKK 17 bn ($2.6bn) in construction of
three new manufacturing facilities as well as
expansion of one existing facility at the
production site in Kalundborg. NNE is Novo
Nordisk engineering partner from design to
construction of this huge expansion, which
signifies one of the largest projects in NNE
history.
Novo Nordisk's investment will establish
additional capacity across the entire global
value chain from manufacturing of active
pharmaceutical ingredients (API) to assembly and
packaging, with the vast majority being invested
in API capacity. These expansions will provide
capacity for the production of Novo Nordisk's
current and future oral and injectable products.
The new facilities will be automated and include
state-of-the-art production technologies
NNE has delivered the conceptual and basic
design for the expansion of the Kalundborg site
and will continue to act as Novo Nordisk's
engineering partner for the coming phases.
Record breaker
CEO of NNE, Jesper Kløve, is proud that Novo
Nordisk has chosen NNE as it's engineering
partner from design to construction, he said:"I
would like to thank Novo Nordisk for entrusting
NNE with the execution of this fantastic
project, which is one of the biggest we have
executed in NNE history. We will do our utmost
to live up to all parameters."
Kløve explains that in the design, NNE have
strived to take account of many different
aspects. First and foremost, the company wanted
to design facilities which are future-proof in
terms of current and future demands for
pharmaceutical production and filled with the
latest technology. At the same time, NNE's focus
has been to create an interior that ensures good
working conditions in terms of space, flow and
light for the employees who will spend their
workdays inside the facilities.
"Moreover, we have strived to achieve an
architectural expression where the buildings
look modern, but without drawing too much
attention. One of the facilities had to fit in
with the existing buildings, while another - the
first large building to be established north of
the railway - had to fit in with fields, railway
and green surroundings," Kløve added. "We have
done our absolute best and the future will tell
if we achieved what we set out to do."
Applying virtual reality in all project phases
NNE has been involved in the project from the
early design phases and has from the beginning
focused on using digital tools to support
project execution and decision processes.
Based on the digital 3D design model created for
the project, NNE has created a collaborative
tool based on virtual reality (VR), which allows
several users to meet virtually inside the 3D
design model and together perform design reviews
and make decisions - regardless of where the
participants are located physically.
In the coming construction phase, NNE will apply
augmented reality (AR) technology, which makes
it possible to review the design model onsite
through an iPad or smartphone by adding a
digital layer of information on top of reality.
This makes it possible to identify and solve
challenges on the spot by simply comparing the
digital design model against the real-world
design.
Britons expect continued collaboration in
(bio)pharmaceutical research
Survey finds British adults expect pharma to
continue to work together to advance both
COVID-19 treatments and innovations for other
diseases.
According to a survey, nearly a third of Britons
are concerned continued COVID-19 vaccine and
treatment research is sidelining innovations and
progress on treatments for other diseases.
Additionally, 28 percent thought pharma and
biotech companies need to play a stronger role
in tackling vaccine inequity.
The research, an online survey of 2,241 British
adults (aged 18 years and older), found that 55
percent of the population expect pharma and
biotech companies to keep working together to
continue developing more
effective COVID-19 treatments and preventive
care. However, 32 percent expressed concerns
that the pandemic is causing researchers to
sideline other key drug treatments/innovations
unrelated to COVID-19.
In addition, the research found that many people
felt their understanding of the pharmaceutical
industry had improved since the start of the
COVID-19 pandemic: 34 percent claimed to have a
better understanding of how
vaccines/treatments are developed and
distributed, 34 percent of the approval process
and 31 percent the use of clinical trials.
However, just 27 percent believed they
understand what messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines
are and how mRNA vaccines work.
Daniel Chancellor, Thought Leadership Director
at Informa Pharma Intelligence, commented: “Over
the last two decades, the number of treatments
being designed using RNA technology
have been slowly rising but were not
widely known outside of scientific circles. The
pandemic has changed this, as both industry and
public recognition of the new vaccine class
has grown – and the mRNA pipeline itself has
tripled since 2019 to become one of the hottest
areas of drug development.
“Excitingly, the application of
mRNA technology extends to the development of
treatments for diseases that have evaded
scientists for some time — take cancer or HIV,
for example. Whilst the development of these is
still in its infancy, highly specialist platform
biotech companies are likely on a trajectory
to producing effective vaccines across a range
of new diseases.”
Half of survey respondents also
believed that COVID-19 had forced pharma
companies to speed up their pace
of innovation in treatment and expect continued
collaboration to expedite drug development in
other areas (such as cancer and infectious
diseases).
The report also reveals that Britons are fearful
of Brexit and other factors disrupting access to
medicines. Among the concerns were Brexit and
border issues (53 percent), heavy goods vehicle
(HGV) driver shortages (48 percent), general
practitioner waiting times (42 percent),
National Health Service (NHS) appointment
backlog (41 percent) and the ongoing effects of
the COVID-19 pandemic (36 percent). Concerns
about Brexit threatening access to medicine and
prescription drugs were significantly greater in
Northern Ireland, with 69 percent of respondents
indicating they were worried.
EMA launches the Regulatory Science Research
Needs initiative
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has issued a
list of about 100 regulatory science topics that
need further research to close gaps and improve
medicine development.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has for the
first time issued a list of
regulatory science topics that need further
research to close gaps and improve
medicine development and evaluation to enable
access to innovative medicines for patients.
EMA has identified around one hundred specific
topics in the Regulatory
Science Research Needs list.
These topics, and the initiative itself, emerged
from the stakeholder consultations which
underpinned the development of the Regulatory
Science Strategy to 2025. EMA carried out
interviews with chairs of its scientific
committees and working parties, and also with
external experts and opinion leaders from the
principal stakeholder groups.
For both human and veterinary medicines, the
topics have been divided into four categories:
·
integration of science and technology in
medicines development
·
collaborative evidence generation to improve the
scientific quality of evaluations
·
patient-centred access to medicines in
partnership with healthcare systems
·
emerging health threats and
availability/therapeutic challenges.
EMA stated that, by publishing this list, it
seeks to stimulate researchers and funding
organisations to consider addressing these
topics in their research agendas and share their
findings and results with regulators. Moreover,
EMA added that, by engaging in the Regulatory
Science Research Needs initiative, researchers
and funders will be able to see their findings
translated into regulatory practice, medicines
development and public health. The list will be
also updated periodically with new topics and
references to related research.
“The acceleration of innovation in medicines
development requires a parallel advancement in
regulatory science,” EMA claimed in the report.
“New technologies and evolving science throw up
new regulatory questions and it is important
that these questions are answered so that
innovation is translated safely and swiftly into
effective, high-quality therapies.
“Addressing the research needs in regulatory
science requires a collaboration with both
academia and key research funding bodies. While
EMA may be able to fund a small portion of the
research needs, external funding obtained by
researchers will remain the primary pathway for
addressing the research topics. To this end, EMA
is committed to fostering a strong working
relationship with European academicians and
researchers as well as key research funding
bodies, as part of the EMA’s Academia Action
Plan,” the report continued.
A webinar to inform patients, academic and
collaborative research groups, and health
professionals is planned on 18 January 2022 to
explain the Regulatory Science Research Needs
initiative and how stakeholders can engage with
it.
ABPI publishes new roadmap to aid in ATMP
development
The roadmap clarifies the processes to develop
advanced therapy medicinal products (ATMPs),
providing guidance on key considerations.
The Association of the British Pharmaceutical
Industry (ABPI) and the Accelerated Access
Collaborative (AAC) have launched a new roadmap
to clarify the processes companies have to go
through to get advanced therapy medicinal
products (ATMPs) to market.
ATMPs, also known as cell and gene therapies,
have the potential to save and transform the
lives of some of the sickest patients and
potentially cure them. However, the processes
involved in getting them to market can be
complex and difficult to navigate.
Recognising their potential, the UK Government
have established initiatives to make
Britain a world leader in the sector;
however, ABPI stated that more can be done to
attract innovators to research, develop,
manufacture and launch their products in the UK.
“Our roadmap helps to demystify the
often-complex processes that innovators face and
is an essential tool for those launching
products in the UK,” explained Dr Paul
Catchpole, Value and Access Policy Director at
the ABPI. It aims to clarify the processes
involved with developing ATMPs and getting
approval, as well as how to engage with the
system.
It highlights four key considerations when
launching a product:
1.
Engage early with all parts of the healthcare
system including the MHRA, NICE and NHS England
– from early product development and regulatory
stages right through to service planning and
commissioning to make sure the system is ready.
2.
Keep the patient in mind throughout and talk to
patient groups to keep them at the heart of
development. Also, consider patient population
diversity.
3.
Take advantage of all available guidance and
support including what’s on offer from the NHS
and other parts of the system partners who can
help you understand the landscape and how to
meet the specific requirements of regulators,
commissioners, and providers.
4.
Aim for simplicity wherever possible and look
for where things can be standardised. The health
service already delivers ATMPs to patients, and
companies should consider what they can do to
make them fit existing systems and processes to
speed up time to market and to patients.
Matt Newman, Deputy Director, AAC, added: “This
is one aspect of a broader programme of work to
ensure that the NHS is ready to adopt the latest
ATMPs, building on the successful introduction
of treatments like CAR-T [chimeric antigen
receptor T-cell therapy].
“Thanks to the new roadmap, ATMP developers have
access to a rich source of information, in one
place, set out in an accessible format. This
first of kind resource will make the end-to-end
pathway for ATMPs easier for developers to
navigate, increase NHS adoption and make the UK
an attractive place to launch ATMPs. Ultimately,
the new ATMP Roadmap will support innovators in
getting ATMPs to NHS patients faster.”
To download the roadmap, click
here.
Plasma-based engineering to accelerate
antimicrobial material development
Could plasma-based engineering provide a greener
method to produce antimicrobial materials, such
as contact-killing, antifouling and drug-release
surfaces?
According to researchers, plasma-enabled surface
engineering could advance antimicrobial material
development, providing a less expensive and more
environmentally friendly method than existing
wet chemistry techniques.
Antimicrobial resistance is
a growing concern worldwide, and particularly
hospital-acquired infections from surgical
tools, implants and heavily touched surfaces.
This has prompted the study of antimicrobial
materials in recent year; however, the existing
wet chemistry methods are often complex, time
consuming and expensive.
In a new tutorial published in in the Journal
of Applied Physics,
researchers from Belgium, Czech Republic, and
Italy present a promising alternative:
plasma-enabled surface engineering.
“Plasma-based engineering is an inexpensive and
environmentally friendly method, because it
doesn’t require the use of solvents and can be
scaled up to industrial production relatively
straightforwardly,” stated co-author Anton
Nikiforov of Ghent University’s Department of
Applied Physics, Belgium.
The technology relies on non-equilibrium plasma,
or partially ionised gas, that produces chemical
reactions to change the properties at the
material surface. The different temperature
levels within the plasma – usually ionised noble
gases, oxygen or air – create distinct chemical
pathways. These reactions can also be
manipulated by adjusting electric power for
surface activation, coating deposition and
surface nanostructuring of virtually any solid
material.
According to the authors, plasma-enabled
engineering can create contact-killing,
antifouling and drug-release surfaces.
Contact-killing materials destroy
micro-organisms through the microscopic spikes
that puncture microorganisms on contact, with
one study demonstrating that plasma-etched black
silicon nanopillar structures were highly
bactericidal against Staphylococcus
aureus, an antibiotic-resistant
bacterium.
Antifouling materials prevent microorganisms
from accumulating on surfaces to form biofilms.
For instance, plasma polymerised
superhydrophobic thin coatings – water-repelling
materials inspired by the lotus leaf – have also
been extensively developed because the lack of
moisture, prevents microorganisms from adhering
to and reproducing on these surfaces.
Drug-release surfaces control the release of
antimicrobial compounds, enabling high-dose
delivery of antibiotics to target locations, an
application that is useful after surgery. For
example, vancomycin, a common antibiotic, was
deposited inside spherical particles using
aerosol-assisted plasma deposition
The scientists explained that numerous
plasma-based methods have been developed to
create such surfaces, including low-pressure and
atmospheric pressure plasma etching, plasma
polymerisation, sputtering, gas aggregation of
nanoparticles, aerosol-assisted plasma
deposition, and various combinations of the same
methods.
However, they cautioned that, despite the
promise of plasma-based engineering, certain
limitations are yet to be addressed, such as
understanding how bacteria adheres to surfaces
and what takes place in the destruction of
microorganisms.
Reliable drug production requires fast and
GMP-compliant labelling
Steierl-Pharma modernizes and optimizes
labelling processes with inspection technology
from OMRON
Hardly any other industry is subject to such
high-quality requirements and legal regulations
as pharmaceutical companies. This applies to
active ingredients, production and storage as
well as to the labelling process. For example,
the labels must be robust and stick reliably for
the usability period of the drug of up to five
years. Labels carry important information such
as the name of the drug, active ingredient(s),
manufacturer, and variable data such as
expiration date, lot number, and serialization
information, if applicable. Establishing a valid
labelling process is key. At the same time, the
processes should also be as efficient, fast and
sustainable as possible.
Steierl-Pharma GmbH from
Herrsching (Bavaria, Germany) relies on the
support of OMRON automation
experts in this regard. By using a new labelling
system with smart camera technology,
Steierl-Pharma can label its pharmaceuticals
with high process speed and reliability. The
labels are printed with variable data on batch
designation, expiration date and if required,
the dispensing notice "Sample not for sale".
Steierl-Pharma is a medium-sized pharmaceutical
company in the field of naturopathy and produces
medicines in liquid dosage form, in cylindrical
glass containers. The product range of the
company, which was founded in 1949 in Munich by
a pharmacist, includes medicines for the
musculoskeletal system, for lowering blood
pressure, for relieving migraines or skin
diseases, or for treating flu-like infections.
In addition, the pharmacists at Steierl-Pharma
are continuously researching new naturopathic
therapies and the use of medicinal plants
ineffective and well-tolerated preparations.
The producer has the legally required
manufacturing license for medicinal products as
well as the GMP certificate. Such Good
Manufacturing Practices (GMP) certification
guarantees process integrity in drug production
and conformity with applicable regulations. When
it comes to filling and packaging the drugs,
Steierl-Pharma uses a production line designed
for around 3,600 units per hour. It consists of
a filling and capping machine, a labeler, and a
packaging machine. The line ensures a continuous
and seamless process consisting of filling and
closing the bottles with a dropper insert and a
screw cap. The closed bottles then leave the
cleanroom and enter the labeler, where they are
labelled and then packed in a folding box
together with an information leaflet in the
packaging machine.
Challenge: Avoiding unintentional machine stops
and read errors
In 2019, a project team at Steierl-Pharma began
initial considerations to introduce a
replacement for an already older labelling
machine. "The labelling machine used until then
already had a smart camera-based inspection
system to check the identity of the label and
the variable data (batch name and expiration
date). However, this had two drawbacks: First,
labels were repeatedly misread as bad labels,
and second, bad units were not rejected, but the
labelling process was stopped. However, this
meant that when the machine stopped, the bottles
backed up into the filling machine, so that it
also stopped, and the packaging machine ran
empty. "So we had a 'bottleneck' in our
process," reports Steffen Wegner, Managing
Director of Steierl-Pharma GmbH.
Requirements: Precision and speed
Wegner explains: "That's why we worked with the
manufacturer HERMA to find a suitable inspection
system. The focus here was on high reliability
and good pricing." The aim was to develop a
labelling machine that on the one hand met the
high requirements in the GMP area, but on the
other hand, also ran without interruption during
regular operation. One of the central criteria
was that the new inspection system should work
particularly precisely: bad units such as an
incorrect or illegible barcode as well as batch
or expiry date errors should be detected
reliably, the keyword being sensitivity. At the
same time, Steierl-Pharma wanted a high level of
specificity: the system should only detect
actual bad units as such and eject them from the
process. But that's not all: with an output of
around 60 labels per minute, the inspection
system only has a time window in the range of
milliseconds for the complex inspection tasks.
FHV7 smart camera supports testing and quality
control
The central component here is the inspection
system. Wegner explains: "We decided on the
OMRON FHV7 smart camera after a test on our
label material on site, supported by an OMRON
application engineer. We were effectively
supported by OMRON throughout the entire
development process up to commissioning and
qualification of the machine and beyond." With
the help of the FHV7, the HERMA labelling
machine at Steierl-Pharma checks the identity of
the label based on the pharmaceutical code and
verifies batch and expiration via OCV (Optical
Character Validation) for compliance with the
specifications. The FHV7 series smart camera
provides illumination and image processing
functionality for enhanced visual inspections.
Due to its world-first multi-colour light and a
powerful high-resolution 12-megapixel camera,
only a single FHV7 camera is needed to perform
high-precision visual inspections of the
production line.
During the performance qualification, which is
part of the qualification of new machines in the
pharmaceutical environment, the project managers
involved were surprised by the extremely high
specificity of the FHV7. "We could not believe
how extremely reliable the OMRON FHV7 inspection
system is. As part of the challenge testing, we
deliberately introduced mislabels, all of which
were reliably detected – but with a throughput
of several 10,000 labels, not a single good
label was incorrectly read as a bad label,"
reports Wegner. Even single faulty units could
cause a lot of trouble in the GMP environment.
By using the new camera, such situations do not
occur, and the machine outages caused by the
incorrect reading of actual good units can also
be prevented.
Another advantage of the OMRON camera, in
addition to its hardware, is the software, which
is intuitive to use and does not require lengthy
training. "I also really like the option of a
customizable user interface, and so do the
users. There is only one window in which, for
example, the target code, batch designation and
expiration date can be entered. Code
verification and Optical Character Validation
(OCV) can also be performed. It's all very clear
and simple," explains Wegner. The software runs
on any current Windows system and communicates
directly with the FHV7 via the local network.
Wegner also praises the high inspection speed of
the OMRON system. The complex individual
inspection of a label takes just 80
milliseconds: "That's impressively fast."
Inspection system and support
"We are very satisfied with both the new labeler
and especially OMRON's inspection technology. In
a highly regulated environment such as the
pharmaceutical industry, manufacturers must be
able to fully rely on the technology that is
used – also to be able to successfully complete
the qualification. This is the case with us,"
Managing Director Wegner sums up. "The
cooperation with the sales and application team
was and is also excellent." Since the company
has had such a good experience with OMRON, it is
planned to convert an existing packaging machine
to OMRON inspection technology within the near
future.
TRexBio Announces Collaboration with Janssen to
Discover Novel Targets for Immunology and
Inflammation
TRexBio Inc. has entered into a multi-year
research collaboration and licensing agreement
with Janssen Pharmaceutica NV, one of the
Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson &
Johnson. This collaboration with Janssen
Research & Development LLC will focus on the
discovery of novel tissue-targeted therapeutics
using TRexBio’s proprietary Deep Biology
platform.
Under the terms of the agreement, TRexBio grants
Janssen an option to an exclusive license to
develop and commercialize therapeutics directed
against selected targets that may arise from the
collaboration, in exchange for an upfront
payment, option fees, milestones and royalties.
TRexBio uses its unique platform to generate
insights into human tissue immune-regulation and
identify novel targets for therapeutics with a
focus on modulating regulatory T cell (Treg)
response. The TRex Deep Biology platform
combines high resolution sequencing of human
tissues, cutting-edge computational biology
tools, and scalable translational biology assay
systems into an optimized workflow, enabling
efficient discovery and functional
characterization of unique tissue-specific
targets.
The companies will use TRexBio’s platform to
discover novel targets that aim to address unmet
needs in immune-mediated disease. Janssen will
be solely responsible for the clinical
development and commercialization of
therapeutics resulting from the collaboration.
“We are extremely pleased to establish this
strategic collaboration with Janssen,” said
Johnston Erwin, CEO of TRexBio. “Our
differentiated Deep Biology platform has the
potential to uncover truly unique insights, and
we look forward to leveraging this collaboration
as part of our mission to bring new medicines to
patients.”
MARKETS
Guardtech Cleanrooms announces corporate
restructuring after acquisition
The company will now operate as five distinct
separate divisions under a broader group
Guardtech Cleanrooms has announced the launch of
the Guardtech Group, made up of five distinct
divisions including the recently acquired
Cleanroom Solutions and the introduction of the
Isoblok.
The remaining three divisions include Guardtech
Cleanrooms, which will now cater specifically
for the modular cleanroom market as well as
CleanCube Mobile Cleanrooms will continue to
provide portable solutions for businesses.
Isopod Rapid Cleanrooms will offer quicker, more
flexible and cost-effective alternatives, using
standardised models made from stock held by the
company, available for flat-pack delivery and
with the option for self-assembly installation.
Guardtech Group Chairman Ray Wheeler said: “As a
board, we’re delighted to make this announcement
– the business has evolved dramatically over the
past five years and we’re so proud of everything
that our team’s hard work has helped us build.
“Like many businesses, we’ve had some tough
obstacles to overcome in that time and we’re
confident this new structure is the ideal next
step to take the company into an exciting phase
of our development. I’d like to thank my fellow
directors and everyone else on the team for all
their brilliant efforts that continue to propel
us towards new horizons.”
Conor Barwise, Guardtech Operations Director,
said: “I’ve been here since the beginning of the
journey and it’s amazing to see how we’ve grown
in that time.
“We’ve had to overcome some serious hurdles, not
least the pandemic in recent years, but the way
we’ve managed to push on in a positive manner is
a reflection of the flexibility and ‘can-do’
spirit of the whole team. I’m proud of
everything the group has achieved so far and
look forward to many more successes in the
future.”
The Group moved to acquire Cleanroom Solutions
late in 2021, having followed the company for
many years. Guardtech Group will now act as the
parent company for five distinct businesses, but
there is scope in the years ahead for even
further additions.
Mark Wheeler added: “Restructuring the business
provided a mechanism to differentiate between
the variety of products and solutions that the
Guardtech Group deliver whilst celebrating the
joint identity and culture that is at the heart
of all of these delivery formats.
“The Guardtech Group is a collective of
long-serving industry professionals that embrace
problem-solving, innovative thinking and embody
a determination to deliver the highest quality
outcomes for a range of valued clients across
the life science industries.
“At the heart of every decision the group makes
is the newly established GUARD Charter,
promoting the core values of guide, understand,
adapt, respond and deliver. Each business within
the Group and every employee working for
Guardtech is held accountable against this
charter and is guided to embody the values that
have made our group strong over its history.”
UK regulator publishes guidance on use of
real-world data to support clinical trials
Two new guidance documents, the first in a
series to published by the MHRA, outline
considerations when planning a randomised
clinical trial using real-world data.
The UK’s Medicines and Healthcare products
Regulatory Authority (MHRA) has published new
guidance on
the use of real-world data (RWD) for randomised
clinical trials.
The two guidance documents were drafted with the
Commission on Human Medicines Real-World Data ad
hoc group following consultation with industry.
They provide considerations when planning a
randomised clinical trial using RWD, with the
intention of submitting this trial to gain a
regulatory approval.
The MHRA stated that using RWD – information
generated during routine healthcare, including
electronic patient health records, and disease
and patient registries – to improve recruitment
and aid regulatory decision-making could
accelerate the development and approval of
life-changing new medicines, making them
available to patients more quickly.
While RWD is frequently used to monitor the
safety of medicines and medical devices after
they have gained approval, it is currently
rarely used to demonstrate the effectiveness of
an intervention before it is approved.
The new guidance is intended to be the first in
a series addressing issues around using
real-world evidence in support of a regulatory
submission. It considers aspects related to
clinical trial authorisation, clinical trial
design (including choice of endpoints and safety
data requirements), and requirements in terms of
database quality and inspection.
The two guidance documents are:
MHRA Guidance on the use of Real-World Data in
Clinical Studies to Support Regulatory Decisions
An introduction to the MHRA’s RWD guideline
series, outlining points to consider when
evaluating whether a RWD source is of sufficient
quality for the intended use.
MHRA Guideline on Randomised Controlled Trials
using Real-World Data to Support Regulatory
Decisions
Guidance on considerations when planning a
prospective randomised trial using RWD sources
with the intention of using the trial to support
a regulatory decision. The guideline covers
clinical trial authorisation (if applying for
approval to run such a trial wholly or in part
in the UK), and clinical trial design including
choice of endpoints and safety data
requirements.
Commenting on the publication, Dr June Raine,
MHRA Chief Executive, stated: “When used in this
innovative way, real-world data has the
potential to make a huge difference when it
comes to bringing medicines through clinical
trials to patients.
“With fewer or even no trial-specific visits,
consenting trial participants do not have to
travel long distances to get to their
appointments. And with fewer logistical hurdles,
real-world data could make it more feasible for
trial sponsors to repurpose existing medicines
for new conditions.
“Because of this, and the growing need to find
more cost-effective ways of conducting clinical
trials, our new series of guidelines focuses on
how to use real-world evidence to aid regulatory
approval, helping to bring medicines to the
patients who need them, sooner.”
Longest Running FDA-approved,
University-associated CDMO in the US
Our experts are here to help clinical and
commercial clients in developing formulations,
manufacturing products, and conducting
analytical testing for sterile and non-sterile
projects.
What we do
Contract pharmaceutical services include:
·
Pre-formulation studies
·
Formulation development (including
lyophilization cycle development)
·
Clinical supply manufacturing and testing
·
Small scale commercial manufacturing and testing
·
Analytical method development and validation
·
Routine quality control analysis
·
Stability studies
·
Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) and
excipient release testing
UI Pharmaceuticals is able to manufacture most
dosage forms including sterile solutions and
lyophilized powders; tablets; capsules; and
non-sterile semisolids and liquids.
Aragen Life Sciences to Acquire Intox Pvt. Ltd.
Enables Aragen to conduct safety assessment
studies from a GLP-certified facility for
submission to regulatory agencies such as the
U.S. FDA.
Aragen Life Sciences, a
global research, development, and manufacturing
services provider, has signed a definitive
agreement to acquire Pune-based Intox
Pvt. Ltd.
This acquisition will expand Aragen’s integrated
discovery and development platform for the
pharmaceuticals, biotechnology ,
animal health and agrochemicals industries. It
will enable Aragen to conduct safety assessment
studies from a Good Laboratory Practice ( GLP )-certified
facility for submission to regulatory agencies
such as the U.S. FDA ,
the U.S. Environment Protection Agency (USEPA),
the European Medicines Agency ( EMA ),
and others globally.
Intox is a GLP certified preclinical contract
research organization ( CRO )
with its test facilities in Pune, India. It has
conducted more than 15,000 GLP studies for
global clients.
The acquisition will also expand Aragen’s
geographical footprint in India. Aragen
currently has research and manufacturing
facilities at Hyderabad, Bengaluru and Vizag in
India and a biologics facility in California,
U.S.
Manni Kantipudi, CEO, Aragen Life Sciences,
said, “Intox’s experienced scientific team has
an excellent reputation for its scientific rigor
and subject matter expertise, and I am delighted
to welcome them into the Aragen family. This
acquisition is in strategic alignment with our
long-term vision to be a ‘one-stop’ integrated
discovery, development and manufacturing partner
to our customers. We can, now, rapidly and
seamlessly, advance promising molecules for our
customers, from early discovery to
Investigational New Drug ( ind )
submissions, making Aragen one of the few global
CROs that can advance programs from “concept-
to- clinic”.
Dr. Narendra Deshmukh, co-founder and Director,
Intox Pvt Ltd. said, “With over two decades of
expertise, Intox is one of the most reputed GLP
facilities in the country, trusted for the
high-quality data generated by our scientists,
which has helped our customers receive approvals
from national and global regulatory agencies
such as USEPA, USFDA, European Commission
amongst others. We are delighted to be a part of
Aragen and believe that the two organizations
bring in complementary capabilities that will
help in delivering long-term value to
customers.”
Genmab Gains Broad Access to Synaffix's ADC
Technologies
Secures rights for conducting research on ADCs
against multiple drug targets under new
licensing agreement.
Genmab and Synaffix have
signed a license agreement providing Genmab
broad access to Synaffix's ADC technologies.
Genmab is granted exclusive research rights to
utilize Synaffix ADC technologies for one drug
target with the option for the worldwide
development and commercialization of the
resulting ADCs. Genmab has the option to
exercise exclusive research and commercial
licenses for additional targets.
For each specific target nominated under the
license agreement, Genmab gains exclusive access
to Synaffix's clinical-stage GlycoConnect Antibody conjugation
technology, HydraSpace polar spacer technology,
as well as select toxSYN linker-payloads, each
designed to enable ADCs with best-in-class Efficacy and
tolerability for the development of multiple
potential therapies.
Genmab will be responsible for the research,
development, manufacturing and commercialization
of any resulting ADC therapies. At the same
time, Synaffix will support Genmab's research
activities, including manufacturing of
components that are specifically related to its
proprietary ADC technologies.
"At Genmab, we are committed to bringing
differentiated medicines to patients, and we
believe collaborations are foundational to
accelerate innovation," said Jan van de Winkel,
Ph.D., chief executive officer, Genmab. "We look
forward to working with Synaffix toward our
shared goal of developing best-in-class or
first-in-class antibody therapies and make an
impact on the lives of patients."
"In what represents our fifth Out-Licensing deal
in the last six months, we are thrilled to
partner with Genmab, an international Biotechnology company,"
said Peter van de Sande, chief executive officer
of Synaffix. "In deploying our cutting-edge ADC
technology platform together with Genmab's
robust antibody development capabilities,
Synaffix is privileged to once more play an
essential role in strengthening a partner's
pipeline with our innovative ADC technologies
thereby aiding the transformation of cancer
treatment."
Under the terms of the agreement, Synaffix will
receive an upfront payment of $4.5 million and,
on a target-by-target basis, is eligible to
receive option-exercise, development-,
regulatory- and commercial milestone payments.
The total potential deal value is $415
million plus tiered, mid-single digit royalties
on commercial sales.
Piramal Pharma Solutions Expands In Vitro
Capabilities at Ahmedabad Site
Multi-million dollar investment to create a
world-class high-throughput screening facility
that will augment existing in vitro biology
capabilities.
Investment augments in-vitro biology
capabilities in primary and secondary screening
at Ahmedabad site.
Piramal Pharma Limited’s Pharma Solutions (PPS) business,
a Contract Research, Development and
Manufacturing Organization ( CDMO ),
has made a multi-million dollar investment to
create a world-class high-throughput screening
facility that will augment existing In
vitro biology
capabilities at its Drug
Discovery services
site in Ahmedabad, India. The expansion, which
is expected to go live in 3Q22, will
significantly add to the primary and secondary
screening capabilities of compounds prepared at
the site.
The benefits of this new investment include
integrated chemistry and biology services from a
single site, with anticipated significant
improvements to drug discovery cycle times. New
personnel with experience in biology services
are also being added to the site team.
The new high-throughput screening technology
enables PPS to evaluate and screen 1000
compounds per week using various Assay platform
technologies such as Fluorescent Imaging Plate
Reader (FLIPR), TR-FRET/HTRF, Fluorescence
Polarization (FP), absorbance, Luminescence/
Electrochemiluminescence (ECL), Alpha Screen,
Lantha Screen, Flow Cytometry, and high content
imaging. These platforms will be applicable to a
variety of targets (e.g., G- Protein -coupled
receptors (GPCRs) and Kinase -targeted
therapies).
Peter DeYoung, Chief Executive Officer, Piramal
Pharma Solutions said, “Assisting customers in
the discovery process is synergistic with our
efforts to be a patient-centric CDMO. With this
investment, we are enhancing our discovery
platform by adding new in vitro biology services
to our existing capabilities, making us a more
integrated partner.”
