
Coronavirus Technology Solutions
April 20, 2020
More Beef Packing Plant Closures
Automation is One Solution for Virus Mitigation
Tyson Using Walk Through Infrared Body
Temperature Scanners
HEPA Air Filtration and UV Treatment in
Elevators
Battelle H2O2 System Can
Decontaminate Masks 20 Times
Several Methods Available for Mask
Decontamination
Are Face Masks the New Condoms?
Hospital Using MSA Respirators With Replaceable
Cartridge
MSA Has a Range of
Respirator Designs Available to Protect Hospital
Personnel
______________________________________________________________________________
More Beef Packing Plant Closures
Several of the country’s largest beef-packing
companies have announced plant closures. Before
the coronavirus hit, about 660,000 beef cattle
were being processed each week at plants across
the United States, according to John Bormann,
program sales manager for JBS, the American
subsidiary of the world’s largest processor of
fresh beef and pork.
This week there probably will be around 500,000
head processed at U.S. plants still in
operation. That’s 25 percent less beef being
produced. Some of the slowdown is because of
facility closures. Two of the seven largest U.S.
facilities — those with the capacity to process
5,000 beef cattle daily — are closed because of
the pandemic.
Absenteeism, fewer employees and spreading out
those remaining employees to maintain social
distance are all also contributing to the slow
down.
JBS USA first closed its Souderton, Pa., beef
plant April 7 and
then shuttered its Greeley,
Colo., beef facility after at least 50 of its
6,000 plant employees tested positive. All have
been urged to self-quarantine.
National Beef Packing Co. announced the closure
of its Tama, Iowa, facility. And Cargill
shuttered production at its Hazleton, Pa.,
ground beef and pork processing plant, and then
reduced production at one of Canada’s biggest
beef-packing plants after dozens of workers
became infected.
Automation is One Solution for Virus Mitigation
One of the leading processed meat and animal
feed producers in Russia Cherkizovo Group
commenced operations of its new meat processing
plant in May 2018.
Located in the suburban town of Kashira in the
Kashirsky District of Moscow, the new plant is
one of the biggest meat processing facilities in
Europe.
The plant has a capacity to process 30,000t of
meat a year. Image

Cherkizovo invested approximately RUR6bn ($100m)
for the plant’s construction, which began in
November 2016. It is one of the biggest
investments to have ever been made in the
region’s food industry.
The new processing plant features
state-of-the-art equipment that produces
high-quality, bio-safe meat products.
With similar designs to plants in the US and
Europe, the plant is one of the first
fully-automated food processing plants Mosco.
The plant also includes warehouses, sausage
packaging lines and thermal cameras, which are
also automated. The plant needs fewer employees
than a traditional plant, only requiring manual
loading and unloading at the beginning and end
of the process.
Designing a fully-automated plant and
integrating it with other company-wide processes
posed challenges for the company, including the
integration of plant manufacturing execution
systems (MES) and enterprise resource planning
(ERP) systems. Cherkizovo plans to implement
these automation systems in future projects to
achieve increased productivity and quality, and
eventually leading to increased competitiveness
and consumer interest.
Cherkizovo is one of the biggest producers of
meat and animal feed in Russia and also one of
the top producers of poultry, pork and processed
meat. Its production facilities include eight
poultry plants, 15 pork units, six meat
processing plants, and nine feed mills.
The new facility complements Cherkizovo’s
existing plants in Moscow, including the
Mosselprom and Petelino poultry production
facilities, as well as the Ozherelye feed mill.
More than 6,000 people from the region are
currently working with the company.
Over the last decade, the company invested
approximately $2bn in the modernization of its
production facilities.
https://www.foodprocessing-technology.com/projects/cherkizovos-meat-processing-plant/
Tyson Using Walk Through Infrared Body
Temperature Scanners
Tyson Foods is using
walk-through infrared body temperature
scanners at three processing plants in an effort
to keep coronavirus out of its sites and
maintain the stability of U.S. food supply.
The scanners can check
employees’ temperature as they walk into the
building.

“Every person that needs to
enter our facility, team member, visitor, anyone
has their temperature taken before they enter
the facility,” Tyson’s senior vice president of
health and safety Tom Brower told CNBC.
Brower said the scanners allow
for mass screening and are faster and more
accurate than handheld devices.
HEPA Air Filtration and UV Treatment in
Elevators
Filtration in elevators has
the advantage over UV of instant capture while
UV takes 30 minutes or more to kill viruses.
This means it is effective when the elevator is
empty for the requisite time and kill surface
pathogens but does not address airborne viruses
when passengers are present. Therefore filter
systems have been developed.
TJHQ series of air purifiers can be installed in
air conditioning or as a space air purifier in
the elevator. It is applicable to hospitals,
shopping malls, office buildings, hotels and
other places. It has been successfully applied
to Shenyang Henglong Plaza, Wuxi Henglong Plaza,
Hangzhou People's First Hospital, Guangzhou
Nansha Central Hospital, Baise City People's
Hospital, Sichuan Institute of Materials and
Technology, Pakistan Electric Power Bureau,
Qinghai Academy of mental Prevention hospitals
and other projects.
With an investment of six million U.S. dollars,
Zhejiang Three Bamboo Technology Co., Ltd. was
established in September 2009 by Hengtai
Environmental Development (HK) Co., Ltd. Three
Bamboo utilizes Hong Kong's mature refrigeration
technology and elevator technology to optimize
elevator car air temperature regulation,
sterilization, decontamination and its service
including research, design, development,
manufacturing, installation and maintenance as a
whole, providing the optimized solution to
elevator car air.
http://zjszkj.com/en/products/kqjhq.asp
Battelle H2O2 System Can
Decontaminate Masks 20 Times
Under a sprawling tent near the small town of
West Jefferson, Ohio Battelle employees have
spent the recent weeks decontaminating over
30,000 used face masks for doctors and nurses on
the front lines of the coronavirus pandemic.

Each day, N95 masks collected from more than 100
hospitals, clinics, fire departments and nursing
homes are treated for hours with a hydrogen
peroxide vapor. Once cleaned, the masks are sent
back to the same facilities to be reused.
Battelle said its process, what they call the
Critical Care Decontamination System, will
eventually be able to clean 80,000 masks a day
per site, and that each mask can be cleaned up
to 20 times before losing effectiveness. Here is
a view inside the decontamination chamber.

Hundreds of employees are involved, and
thousands more are being hired, with many going
through training to set up decontamination sites
on Long Island and in Seattle, Boston,
Washington, D.C., and elsewhere.
Several Methods Available for Mask
Decontamination
Several methods are effective at killing the new
coronavirus on N95 masks — primary protective
gear for health care workers — for two or three
rounds of use.
One method is UV treatment. The McIlvaine
Mask Reuse Webinar covered the successful use at
the U. of Nebraska hospital shown below.

The new research,
done at the Rocky Mountain Laboratories of the
National Institute of Allergy and Infectious
Diseases and used live novel coronavirus,
formally known as SARS-CoV-2, to
test the mask material. The study determined
which decontamination procedures were most
effective, and how they affected the integrity
of the masks.
Dr. Vincent Munster and his colleagues tested
four methods of killing the virus: UV light, dry
heat, vaporized hydrogen peroxide (VHP) and
ethyl alcohol. Of those methods, they did not
recommend ethyl alcohol because although it
killed the virus, it degraded the mask material.
Vaporized hydrogen peroxide, a method often
available in large hospitals, was effective, and
left the masks still functioning for at least
three rounds of decontamination, as did UV
light.
Dry heat, at 70 degrees Celsius or 158 degrees
Fahrenheit, was effective, but the masks
withstood only two rounds of decontamination.
Dr. Munster said that “vaporized hydrogen
peroxide would be the method of choice if that’s
available.” However, he said, a nursing home
might not have that, while for dry heat, what’s
needed is basically an oven.
Another recent study from Canadian researchers,
also not yet peer reviewed, confirmed the value
of decontamination. It included masks of
different brands and found that the material of
the mask was still effective after 10 rounds of
vaporized hydrogen peroxide decontamination.
https://www.nytimes.com/2020/04/16/health/n95-masks-decontaminated-coronavirus.html
Are Face Masks the New Condoms?
This is the question posed by James Gorman of
the NY Times
If people with no symptoms are spreading
the coronavirus, as some studies suggest, it may
be time to give face masks the kind of
advertising and promotion that support condoms
as lifesavers.
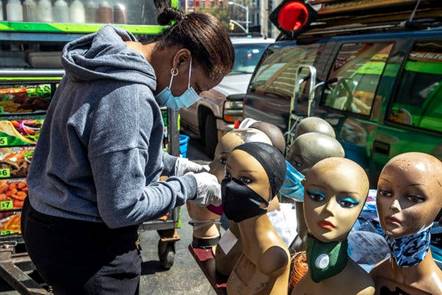
A face mask vendor in West Harlem in Manhattan
on Thursday .Credit...Brittainy
Newman/The New York Times
Dr. David O’Connor, who researches H.I.V. and
other viruses at the University of
Wisconsin-Madison said some recent research had
shifted his thinking about the current pandemic.
“H.I.V. is also spread while people feel fine,”
he wrote in an email, “and consistent, correct
condom use is a barrier to sexual virus
transmission that works.”
He said it was time to “normalize face masks,
and fast.”
“Kids are going to need to wear them to school
when classes resume,” Dr. O’Connor said. “Adults
are going to need to wear them to work. If you
want to go to a basketball game, when we get to
that point, face mask. They need to be as
ubiquitous as Kleenex, as quickly as possible.”
And they should probably be fashionable as well,
he said, with celebrities promoting them.
https://www.nytimes.com/2020/04/18/health/coronavirus-mask-condom.html
Hospital Using MSA Respirators With Replaceable
Cartridge
Health care workers in the Allegheny Health
Network have started using protective gear that
is expected to replace thousands of N95 masks.
AHN
has partnered with Pittsburgh-based company MSA
Safety to secure a shipment of P100
industrial-grade respirators, the health network
announced Thursday.
The
masks are reusable and can be disinfected. When
the coronavirus subsides, the masks can be
stored and used again if needed, officials said.
They will be used by intensive care unit and
emergency department staff, as well as
caregivers working with patients who are
confirmed or suspected to have the coronavirus,
throughout the AHN system.
The
MSA Advantage 200 LS Respirator style was
selected by AHN staff for its fit and comfort,
said Dr. Sri Chalikonda, AHN’s chief medical
operations officer.
Employees who are currently using multiple N95
masks per day will be prioritized, he said.
The
initial shipment includes 4,000 masks.

The
P100 masks, which are not typically used in
health care settings but are approved for
industrial use by the National Institute for
Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), cover a
person’s nose and mouth, and are equipped with
two removable filter cartridges.
They will be sterilized between uses.
“MSA recognizes that fighting the spread of
COVID-19 requires an all-hands-on-deck
approach,” said Steve Blanco, President of MSA’s
Americas business segment. “We are pleased to be
working alongside AHN and other leading health
care providers to explore and deliver PPE
solutions that are helping communities better
respond to this unprecedented challenge.”
The
U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
approved the use of such respirators in health
care settings during the coronavirus pandemic in
early March.
MSA Has a Range of
Respirator Designs Available to Protect Hospital
Personnel
The CDC has specified that
reusable National Institute for Occupational
Safety and Health (NIOSH)-approved elastomeric
respirators are a viable option for use by
healthcare workers and the first responder
community. This document outlines MSA Safety’s
NIOSH approved respirators and filter
configurations that meet CDC’s guidance. Two key
considerations when selecting an air-purifying
respirator (APR) for protection against COVID-19
are respirator type and protection level. While
there are many types of respiratory protection,
CDC recommends NIOSH-approved masks with a
protection factor of N95 or higher for certain
healthcare workers who may be exposed to
COVID-19. In the link MSA provides a comparison
of respirator types, including supplied-air
respirators; filter classifications regulated by
NIOSH that meet CDC recommendations;
