|
|||||||
|
|
|||||||
|
· Market for Gas Turbine Air Treatment to Exceed $10 Billion In 2014
· Complex Mercury Decisions for Power, Cement and Waste-to-Energy Plants Are Simplified With GDPS
· Renewable Energy Briefs
· Headlines for the September 20, 2013 - Utility E-Alert
· “Update on Coal Ash and CCP Issues and Standards” will be the “Hot Topic Hour” on Thursday, October 3, 2013
· McIlvaine Hot Topic Hour Registration
Market for Gas Turbine Air Treatment to Exceed $10 Billion In 2014
In 2014 operators of gas turbines will spend $10 billion for air treatment. This includes treatment expenditures for 90,000 MW of new systems. It also includes service and consumables for 1.4 million MW of turbine systems in place. These are conclusions reached in a special study conducted by the McIlvaine Company. Gas turbines are increasingly used for power generation by large utilities. They are also used for power and steam generation by a number of industries.
Expenditures for air treatment have been rising at close to double-digit rates. One reason is the successful competition with coal. Another is the willingness of operators to obtain better filtration of the inlet air. The third factor is tougher regulations on NOx, particulate, VOCs and CO.
The market includes the following products and services:
|
Gas Turbine Air Treatment Products and Services |
|
|
Capital |
Operating and Maintenance
|
|
Intake Housing |
|
|
Weather Protection |
|
|
Conditioning |
Nozzles |
|
Pre-filtration |
Filters |
|
Coalescers |
Coalescers |
|
Final Filtration |
Filters |
|
Tempering Air System (Single Cycle) |
Dampers, Drives, Fan Parts, Seals |
|
Duct Burner (Combined Cycle) |
Burner Parts |
|
Ammonia Injection Grid |
Nozzles, Ammonia |
|
CO Reactor |
Catalyst |
|
SCR |
Catalyst |
|
Process Controls |
Sensors, Valves, Seals, Gaskets |
|
CEM |
Rata Testing, Protocol Gases, Instruments |
|
Silencer |
Silencer Parts |
|
Stack |
|
For more information on this special study contact: editor@mcilvainecompany.com.
Complex Mercury Decisions for Power, Cement and Waste-to-Energy Plants Are Simplified With GDPS
The U.S. and China have new laws requiring power plants to reduce mercury. Many countries have laws governing mercury reduction from waste-to-energy power plants and certain other sources. The U.S. has also just issued requirements for industrial boilers and cement plants.
The technology selection necessitates utilization of a number of decision trees and a route which includes some back tracking. Obtaining the right sequence and utilizing decision trees with all the needed fruit will ensure the best decision.
Mercury Reduction Global Decisions
Positioning System™ (GDPS)
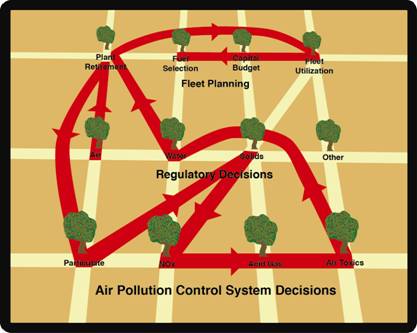
The Mercury Reduction Global Decisions Positioning System™ (GDPS) is a route map to the right sequence of decision trees in the Global Decisions Orchard. The potential cost of mercury reduction forces a decision as to whether to retire the plant. The next decision tree stop will be Particulate. The reason is that any mercury decision involves the particulate control technology. This is so complex that even U.S. EPA is confused.
Because uncontrolled mercury emissions are virtually all gases, the regulation only requires stack measurement of mercury gas emissions. Many of the control schemes rely on converting mercury to a particulate form and then capturing it. The result is that significant percentages of the emissions are in the particulate state.
There are considerations relative to the parallel need to reduce SO2, HCl, NOx and cadmium. There are implications relative to wastewater quality and solids by-products.
The Mercury Reduction GDPS is a continually updated system which is designed for the power plant decision maker. Mercury Air Reduction Markets is a guide and strategic planning tool for suppliers.
If you are an employee of a power, waste-to-energy, or cement plant and would like free access to the Mercury Reduction GDPS, just provide your title and e-mail and send to; editor@mcilvainecompany.com with this message. “Please provide access to the Mercury Reduction Global Decisions Positioning System™”.
For more information on Mercury Air Reduction Markets, click on: http://home.mcilvainecompany.com/index.php/markets/2-uncategorised/85-n056
Renewable Energy Briefs
Siemens Inaugurates New, State-of-the-Art Wind Service Training Center in Orlando
Siemens Energy has formally inaugurated its new, state-of-the-art wind service training center in Orlando, FL.
Siemens currently provides service and maintenance for more than 3,000 installed turbines in the Americas region and 6,800 globally, with a combined generating capacity of 15 gigawatts (GW). As more wind energy projects come online in the U.S. and across the region, highly skilled technicians will be needed to provide the long-term service and maintenance required to help insure the turbines operate at peak production, availability and reliability levels. The new Orlando training center contributes to that long-term need, providing trainees with the industry’s highest level of safety training and equipping them with the advanced technical skills needed to service and maintain wind turbines. Siemens will also train the technicians who work on the installation of wind turbines in the Americas, with training specifically designed to address the installation process and related safety requirements. In addition, the advanced training at the center will be made available to technicians from Siemens’ wind power customers.
Built based on LEED Gold green-building standards, the new 40,000-square-foot building is located close to the global headquarters of Siemens’ Energy Service division and features the latest Siemens’ wind technologies which are used in the hands-on safety and technical training. Two full-size nacelles (the generator portion of a wind turbine), three 30-foot high climbing towers, ladder structures, electrical and hydraulic modules, and a service crane station are located within the center, making training, safety and rescue simulations as realistic as possible. A number of technologically equipped training labs and flexible space to accommodate varying class sizes are also available at the training center.
The new center will host more than 2,400 trainees annually from the U.S. and the Americas and is located close to Orlando International Airport, allowing for easy access for visiting technicians.
1,700 Dutch Households Jointly Buy Their Own Wind Turbine and Set New Crowdfunding World Record
Within a record time of just thirteen hours, all 6,648 shares in a Dutch wind turbine were sold to 1,700 households. The transaction, facilitated by the Windcentrale, raised €1.3 million in an astounding new crowdfunding world record. For the next 12 years, these new 'wind-sharers' will receive their own sustainable energy from a modern large-scale wind turbine. In total, the Windcentrale has facilitated more than 6,900 Dutch citizens to jointly share wind turbines. Waiting lists for additional aspiring Wind-sharers are accumulating rapidly.
The wind shares were sold for €200 each and households bought single shares or blocks of shares. Each share corresponds to approximately 500 kWh of electricity per year (the annual average household consumption in the Netherlands is 3500 kWh).
The Windcentrale was founded in 2010 and aims to accelerate the switch to sustainable energy in the Netherlands. With the Windcentrale setting up cooperatives that own a wind turbine, participating wind-sharers become the joint owners of the wind turbine, and consume their own electricity. A dedicated smartphone App allows every owner to see wind speeds and electricity production levels 'real time'. In this crowd-funded investment, wind-sharers bought a Vestas V80 2MW turbine from 2005 that will provide them with clean electricity for the next 12 years. Next to the price of the wind-share, they will pay an annual turbine maintenance fee of €23 per year. Even if electricity prices do not increase structurally over the next 12 years, the wind shares will still enjoy lower electricity costs than traditional energy consumers. With electricity levels likely to rise however, the wind-sharers will enjoy significant annual cost savings.
Energy Capital Group Announces 300 MW Solar Plant in Millard County, Utah
Energy Capital Group, LLC (ECG) is developing ECG Utah Solar 1 a 300 MW solar plant adjacent to the Intermountain Power Plant (IPP). This will be one of the largest solar projects built and cost an estimated $600 million. ECG is leasing 1754 acres from the Utah School and Institutional Trust Land Administration (SITLA). The location is ideal as the infrastructure includes a HVDC transmission line going directly to California.
The project will create approximately 200 construction jobs, power an estimated 80,000 homes, generate substantial tax revenue for local & state government, will benefit Utah’s K-12 grade school children through lease payments to SITLA and provide clean affordable energy.
Ex-Im Bank Approves $34 Million to Finance the Export of U.S. Solar-Related Products to Spain and South Africa
As part of its renewable-energy push, the Export-Import Bank of the United States (Ex-Im Bank) has authorized a pair of direct loans totaling $33.6 million to Abengoa of Seville, Spain, that will facilitate the export of American heat-transfer fluid produced by The Dow Chemical Company for use in solar projects in Spain and South Africa.
Ex-Im Bank's financing will support approximately 200 U.S. jobs, according to bank estimates derived from Departments of Commerce and Labor data and methodology.
Power Africa is a new initiative to double access to power in sub-Saharan Africa. In its initial phase, the U.S. has already committed more than $7 billion in financial support to this effort.
DOWTHERM™A heat-transfer fluid from Dow is a Key component of the steam-heating process in concentrated solar power plants and replaces conventional fossil-fuel boilers.
Abengoa is an international company based in Seville, Spain, that applies innovative technology solutions for sustainability in the energy and environment sectors. The company operates two parabolic-trough solar plants in Logrosan, Spain, and is currently building two plants in the Northern Cape Province of South Africa with the Industrial Development Corporation. The two plants in Spain and one of the two in South Africa will rely upon DOWTHERM A.
Andritz to Supply Major Equipment for Mjölby Biomass Power Plant in Sweden
Andritz Energy & Environment (AE&E), part of international technology Group Andritz, has received an order from energy utility Mjölby-Svartadalen Energi (MSE) to supply a biomass-fired combined heat and power plant for the town of Mjölby, Sweden. Start-up is scheduled for the third quarter of 2015.
The scope of supply comprises an EcoFluid bubbling fluidized bed boiler with a capacity of 35 megawatts, the fuel handling and flue gas cleaning systems, as well as a steam turbine with all auxiliary systems. The high efficiency of the Andritz boiler plant and the modern technology to enhance environmental protection were decisive in the award of this order.
The new biomass power plant will supply renewable, clean energy for the district heating supply to the town of Mjölby (26,000 inhabitants) in southern Sweden.
For more information on Renewable Energy Projects and Update please visit
Headlines for the September 20, 2013 – Utility E-Alert
UTILITY E-ALERT
#1143 – September 20, 2013
Table of Contents
COAL – US
§ EPA proposes Carbon Standards for New Power Plants
§ Appeals Court refuses Request to Delay installing Emissions Control at Cholla, Coronado and Apache
§ Foresight Energy proposes paying for FGD System at Newton, in exchange for Long-term Contract for Illinois Coal
§ Jeffrey Energy Center to Upgrade NOx Control System
§ AEP to retire entire Tanners Creek Plant in Indiana
COAL – WORLD
§ Locals stall $4 Billion Indonesia Power Plant
§ National Hydro Electric Power to take over 1,320 MW Sarguja Power Project in Chhattisgarh, India
§ Construction starts in Indonesia for MicroCoal’s Commercial Coal Upgrading Facility
GAS/OIL – US
GAS/OIL – WORLD
NUCLEAR
BUSINESS
§ Wood Group GTS to supply GE LM6000 Controls System to 615 MW Apache
§ Clean Coal Technologies, Inc. to locate Pilot Plant at Oklahoma Power Plant
§ Air Quality IX October 21-23 will aid in your MATS Decisions
§ Liquid and Air Filter Element Sales will exceed $34 Billion this Year
§ The World Market for Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP) Systems, Repair Parts and Service will exceed $16 Billion in 2014
HOT TOPIC HOUR
§ Air Pollution Control (APC) for Gas Turbines - Hot Topic Hour September 19, 2013
§ “Multi-pollutant Control Technology” will be the Hot Topic on Thursday September 26, 2013 and again on Friday September 27, 2013 both starting at 10 a.m. CDT
For more information on the Utility Tracking System, click on: http://home.mcilvainecompany.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=72.
“Update on Coal Ash and CCR Issues, Standards and Solutions” is the of the “Hot Topic Hour” on October 3, 2013
On July 26, 2013 the House of Representatives voted 265-155 to allow States to regulate coal-fired power plant byproducts (commonly referred to as Coal Combustion Residues or CCRs). This legislation would halt the EPA's effort to regulate coal ash as a hazardous waste. The bill, sponsored by West Virginia Republican David McKinley, would set minimum federal standards for the management and disposal of CCRs. The EPA would be responsible for certifying state programs and states could implement standards more stringent than those set at the federal level. The Senate, however, has failed to pass any comparable legislation.
Therefore, if the EPA adheres to their schedule, new proposed regulations for CCRs will be issued in October. CCRs include bottom ash and flyash, boiler slag and SO2 scrubber waste. The EPA's original proposal outlined two options for regulation: one approach would regulate coal ash as a "hazardous waste" under Subtitle C of the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA), while the other approach would involve regulating coal ash as a nonhazardous waste under RCRA Subtitle D. Which it will propose next month is yet unknown. All of the discussion about regulating CCRs as hazardous waste has attached a stigma to beneficial re-use. After growing for ten years to a level where in 2009, 44.3 percent of CCRs were recycled to industry as raw materials, the rate is now declining.
Although the future is very uncertain, the increasing cost of disposing of the approximately 130 million tons of CCRs generated annually and lawsuits by environmental organizations and others are causing coal-fired power plant operators to look for ways to reduce CCRs generated and to convert more of them to beneficial income producing uses rather than waste. For many years, power plants have been successfully selling flyash for use in Portland cement, concrete and concrete products, road base and structural fill material and soil stabilization and selling FGD gypsum for making wallboard and as an agricultural soil amendment and source of plant nutrients, calcium and sulfur. And new uses for CCRs continue to be developed.
The following speakers will address the status of proposed EPA regulations, congressional actions and state regulations and the lawsuits related to them, the potential impacts of the eventual regulations on the coal-fired power plant industry and technology to reduce the volume of CCRs generated by plant processes as well as the issues related to beneficial use of coal combustion byproducts such as economics, regulatory or other impediments, potential GHG reductions, market situation and potential uses for coal-fired power plant wastes, the available technology for production of beneficial byproducts, present case histories of successful operations and ongoing research and development of technology to produce or market byproducts of coal combustion.
Ron Grabowski, Vice-president Business Development at Clyde Bergemann Power Group Americas, Inc., Materials Handling Product Division, will discuss the handling of bottom ash. Today's coal-fired power plants are faced with aging bottom ash systems and uncertain environmental regulations look to the industry for solutions. This presentation will examine the options available to handle bottom ash without the use of ash pond storage.
Dale Timmons, R.G., Business Development Program Manager at NAES Corporation, will discuss Circumix Dense Slurry System (DSS) technology. The EPA's proposed rule changes for Coal Combustion Residues (CCR) and Effluent Limitations Guidelines (ELG) are changing how coal-fired power plants need to handle combustion byproducts and wastewater. NAES Corporation and GEA EGI have teamed to deploy Circumix Dense Slurry System (DSS) technology in North America. DSS is a proven and commercially deployed technology that uses wastewater (including FGD water) to stabilize ash products. The process results in: 1) zero discharge of transport water, 2) a non-dusting product, 3) a solid product exhibiting low hydraulic conductivity, high compressional strength and satisfies all of the challenges presented by the proposed CCR and ELG rules. This process is less expensive than traditional "dry" ash management systems and facilitates use of existing plant infrastructure for ash management conversion. Details regarding the historical use, performance data and processing details will be discussed.
Douglas J. Dahlberg PE, Project Associate II at Sargent & Lundy LLC, will present “Proposed U.S. EPA Coal Combustion Residual Regulations - Maximize and Transition Your Existing Disposal Site.” The electrical generating community is well aware of the 2010 U.S. EPA-proposed first-time nationwide regulations for disposal of CCRs. Since the proposed rule was published, a flurry of bills introduced in the U.S. Congress are steering the final rule to classify CCRs under Subtitle D, Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA), similar to Municipal Waste. The June 7, 2013 Code of Federal Regulations, Effluent Limitations Guidelines (ELG) and Standards for the Steam Electric Power Generating Point Source Category Proposed Rule stated: “reliance on (current) data… coupled with the ELG proposed requirements could provide strong support for a conclusion that regulation of CCR disposal under Subtitle D would be adequate.” Speculation on final regulation publishing timing ranges from October 2013 to the end of 2014.
We know new disposal site construction requirements and estimated costs. The critical question for a power plant is “how do you transition your current disposal operation with minimum impacts and expense?” Timely budget planning, decisions and actions are necessary to ensure a smooth transition. Whether your current disposal operation is wet or dry bottom/flyash/FGD byproducts, above or below grade, permanent disposal or transfer, your basic choices include:
This presentation will present an up-to-the moment rule status summary, critical points of the CCR proposal with regard to existing operations and offer engineering solutions available for compliance and plant transition, and suggestions as to how best utilize your existing disposal site. Each site is unique and so will be your disposal decision.
To register for the October 3, 2013 “Hot Topic Hour” on “Update on Coal Ash and CCP Issues and Standards” at 10 a.m. CDT, click on: http://www.mcilvainecompany.com/brochures/hot_topic_hour_registration.htm.
McIlvaine Hot Topic Hour Registration
On Thursday at 10 a.m. Central time, McIlvaine hosts a 90 minute web meeting on important energy and pollution control subjects. Power webinars are free for subscribers to either Power Plant Air Quality Decisions or Utility Tracking System. The cost is $125.00 for non-subscribers. Market Intelligence webinars are free to McIlvaine market report subscribers and are $400.00 for non-subscribers.
|
DATE |
Non-Subscribers Cost |
SUBJECT |
Webinar Type |
|
October 3, 2013 |
$125.00 |
Update on Coal Ash and CCP Issues and Standards |
Power |
|
October 17, 2013 |
$125.00 |
Air Pollution Control in China |
Power |
|
October 31, 2013 |
$125.00 |
Chinese FGD/SCR Program and Impact on the World |
Power |
|
November 21, 2013 |
$125.00 |
Wet vs. Dry ESP |
Power |
|
December 5, 2013 |
$125.00 |
Update on Gasification Projects and Technology |
Power |
|
December 12, 2013 |
$125.00 |
Selecting FGD Scrubber Components |
Power |
|
December 19, 2013 |
$125.00 |
Application of U.S. Mercury Control Technology in Other Countries |
Power |
On Thursday at 10 a.m. Central time, McIlvaine hosts a 90 minute web meeting on important energy and pollution control subjects. Power webinars are free for subscribers to either Power Plant Air Quality Decisions or Utility Tracking System. The cost is $125.00 for non-subscribers. Market Intelligence webinars are free to McIlvaine market report subscribers and are $400.00 for non-subscribers.
To register for the “Hot Topic Hour”, click on:
http://www.mcilvainecompany.com/brochures/hot_topic_hour_registration.htm.
----------
You can register for our free McIlvaine Newsletters at: http://www.mcilvainecompany.com/brochures/Free_Newsletter_Registration_Form.htm.
Bob McIlvaine
President
847 784 0012 ext 112
rmcilvaine@mcilvainecompany.com
191 Waukegan Road Suite 208 | Northfield | IL 60093
Ph: 847-784-0012 | Fax; 847-784-0061